What is Bear and bull markets
Introduction
The terms Bear and Bull Markets are often used to describe general actions and attitudes either of an individual asset or the market as a whole.
While the terms are easy to understand, the impact either a bull or bear market can have on your portfolio and wealth is undeniable.
Although the origins of these Bear and Bull Markets terms are unclear, the most common explanation is derived from the way in which each animal attacks its opponents.
A bull will thrust its horns up into the air, while a bear will swoop down. These actions have been metaphorically attributed to the movement of a market.

If the trend is up, it is considered a bull market and if the trend is down, it is considered a bear market. So how exactly can we define Bear and Bull Markets?
Bull Market
Defination
A bull market or bull run is defined as a period of time in which the majority of investors are buying.
At this time, demand outweighs supply, market confidence is high and prices are rising. Investors who believe that prices will increase with time are referred to as bulls.
Essentially, the term bull market is used to refer to the stock market, however, it can also be applied to anything that is traded; like bonds, real estate commodities and currency.
CAUSE
- The term is usually reserved for extended periods in which a large portion of security prices are rising. This is because prices of securities are continuously rising and falling during trading. These markets tend to last for months or even years.
- Bull markets generally occur when the economy is strengthening or when it is already strong.
- They tend to happen in line with strong gross domestic product and reductions in unemployment, and will often coincide with a rise in corporate profits.
- Investor confidence also rises during this time and the overall demand for stocks is positive together with the overall tone of the market.

EFFECT
- During these markets; Investors buy more stocks because their prices have been increasing, investors are convinced they’ll keep doing so and therefore, they keep buying.
- Due to supply and demand, the prices are raised even higher.
- Companies bet more on their companies. Buoyed by consumer buying, businesses make more investments which usually means hiring more workers and paying existing employees more money.
- Rates of unemployment decrease. Average wages go up as companies compete for workers. Workers are more likely to search for new jobs since they have a better chance of finding one that pays more.
- Inflation also occurs. Money is easier to spend as it feels like it will be relatively easy to get. All of this spending may lead to an immense increase in prices.

Types of bull markets
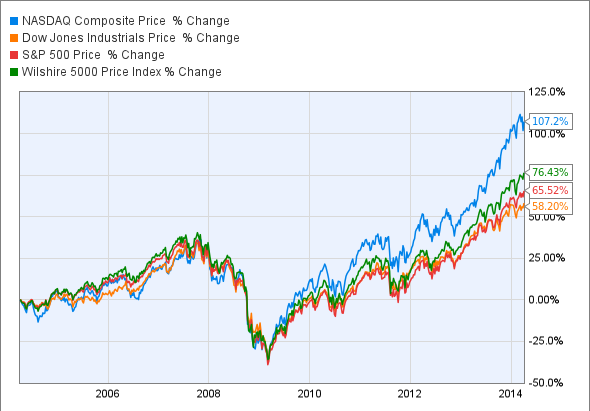
Stock
All three major stock market indexes rise at the same time and these include
- S&P 500,
- Dow Jones Industrial Average
- NASDAQ.
A bull market consistently makes higher highs and higher lows.
A stock bull market occurs in a healthy economy and a stock bull investment is driven by top-line revenue, profit and price-to-earnings ratio.
Gold
Gold bull markets have historically occurred during bull stock markets.
This makes gold an effective hedge against other investments and a method of diversifying an investment portfolio and a proven safe haven in times of economic turbulence.
It is therefore often advised that investors should allocate five percent or more of their portfolio to gold or other precious metals.

Bonds
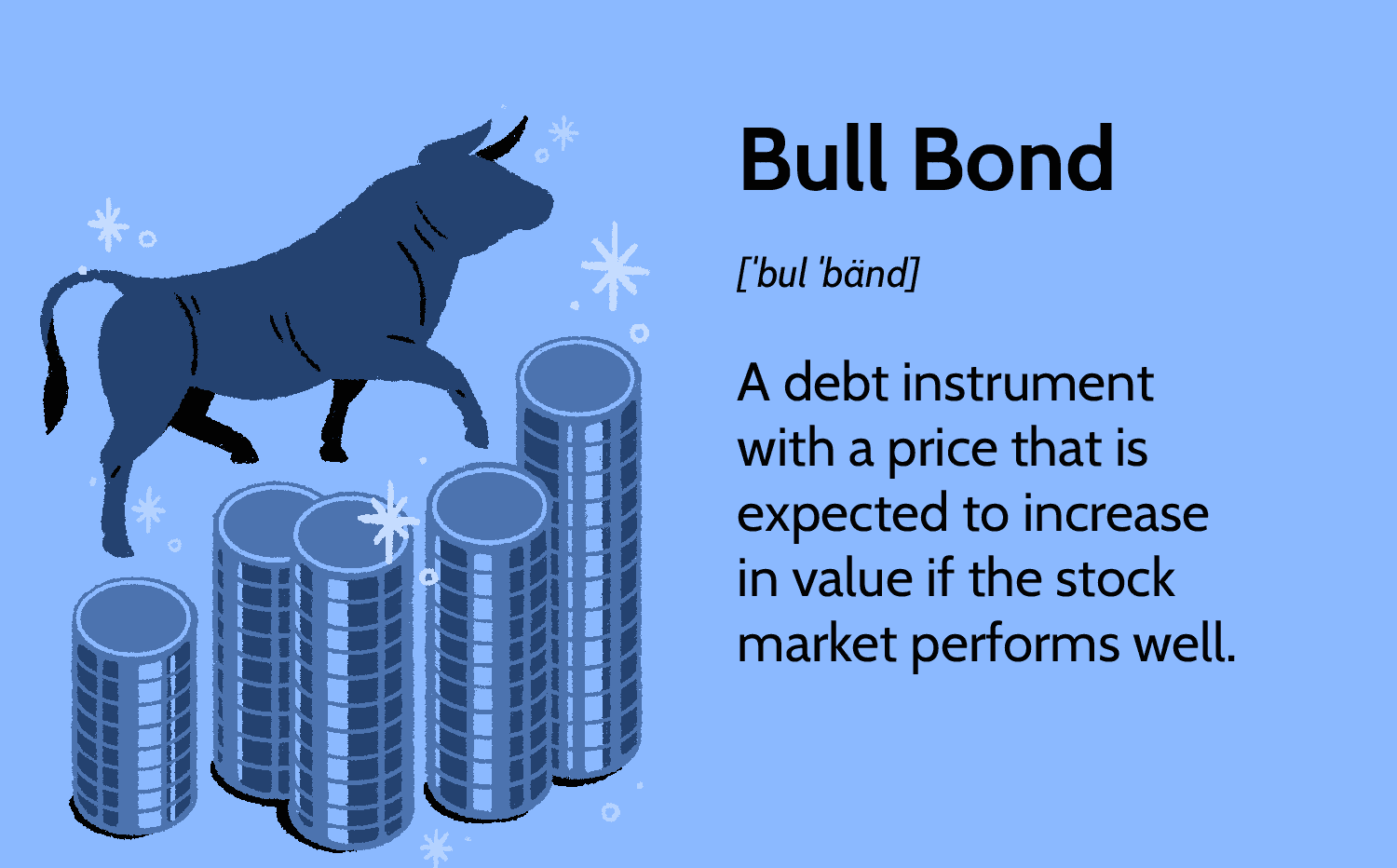
Since the mid-1980’s bonds have been bullish which means that investors have not lost money when buying a bond because their rates of return were always positive.
A bull bond is a debt instrument with a price that is expected to increase in value if the stock market performs well.
Many believe there is a correlation between stock and bond prices such that when stocks go up bonds tend to go down, and vice-versa.
With a bull bond, however, this correlation is positive. Certain fixed-income insecurities are structured in such a way that makes them bull bonds.
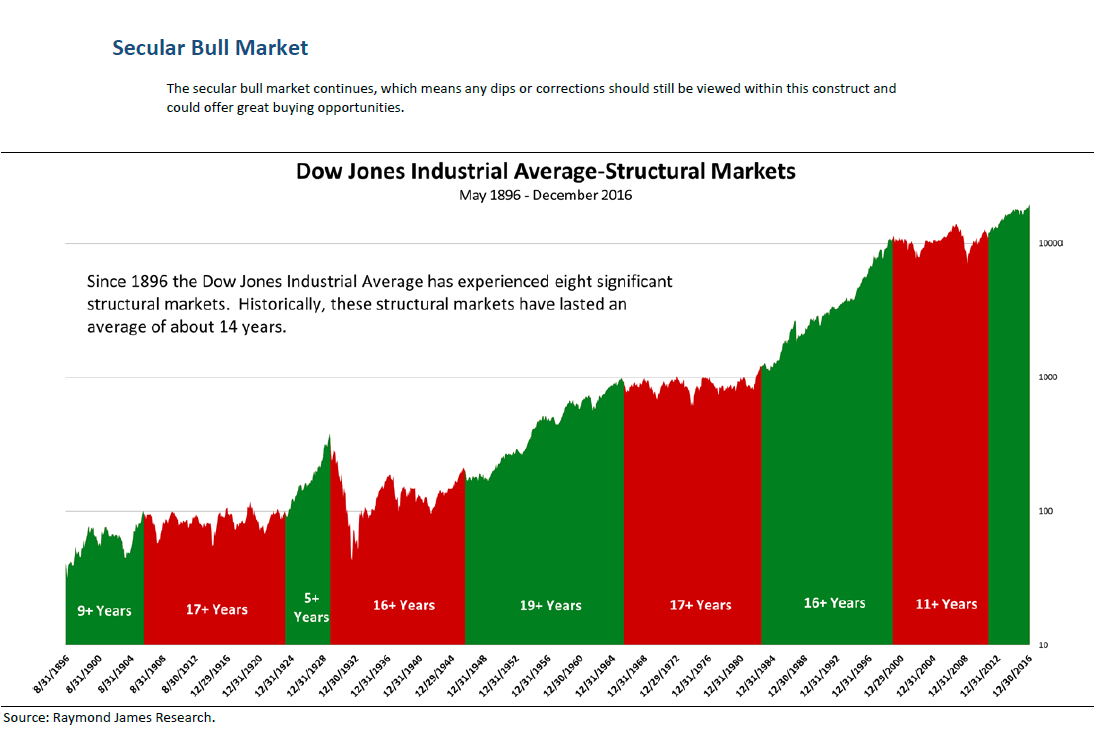
A secular bull market is a long-term trend that lasts five to twenty years.
A bull market can experience a market correction and then resume its upward swing without entering a bear market.
A secular bull market can have smaller bear markets within it known as primary market trends and occur often.
Examples of bull markets throughout history
Post world-war II Rally
- This took place from 1949 to 1956.
- The S&P 500 rose 267% over 86 months, which works out to a commendable annualised return of twenty percent. Consumer goods were the main drivers and also a strong export market helped companies grow.
- However, all this came to an end because the Fed raised interest rates and international tension helped bring on a bear market.
Housing boom
- This occurred between 2002 and 2007.
- The housing bubble began after the federal government reduced interest rates in the hopes of encouraging investment.
- The financial institutions that encouraged real estate investing, home financing and trading in mortgages performed extremely well, until interest rates started to rise again and borrowers started to default. This resulted in the mortgage crisis.
The longest bull run in history
- This record-breaking bull market lasted from 2009 to 2020 – nearly eleven years – making it the longest in history.
- The S&P 500 gained over four hundred percent after a low of 666 points in March 2009.
- In February 2020 the Dow Jones Industrial Average reached a record high of 29,551 points.
- The gains for the S&P alone amounted to over eighteen trillion on paper.During this period, unemployment was at a forty-year low.
- Even during a bull market there will be dips, fluctuations and corrections. Misinterpreting short term downward movements as the end of a bull market is easy.
That’s why it’s important to consider any potential signs of a trend reversal in Bear and Bull Markets from a broader perspective by observing price action over a long period of time.

Precaution during bull market
- The past has shown that bull markets don’t last forever and investor confidence will begin to decline at some point. This could be triggered by anything from unfavourable legislation to unforeseen circumstances such as the pandemic.
- Sharp downward movement of prices can start a bear market where more investors are under the impression that prices will continue to fall, causing them to sell to prevent further losses.
- A bull market generally lasts until prices have risen for so long that investors begin to believe that prices will continue to increase.
- When prices fail to fall over time, investors enter a state of irrational exuberance. They start bidding prices above the actual underlying value, over-valuing the investments.
- This creates an asset bubble where prices rise until the supply of the assets resists any more rise in price. The moment investors begin to panic and sell, the bubble bursts and prices start to fall.
- If prices fall ten percent or less, it’s considered a market correction.and at twenty percent investors are distraught as the bear market begins.
Bear markets

Defination
The opposite of a bull market is a bear market. It is characterised by falling prices and is typically shrouded in pessimism.
It’s not easy to consistently predict when the trends in the market might change. This is partly due to psychological effects and speculation that may sometimes play a large role in the markets.
Cause
A bear market is when a market experiences prolonged price declines.
It typically describes a condition in which securities fall twenty percent or more from recent highs amid widespread pessimism and negative investor sentiment.
If the economy is affected enough, bear markets can sometimes lead to a recession. They can last a few months to a couple of years, but the economy is not viewed as being in recession until the National Bureau of Economic Research decides that specific conditions have been met.
Effect
- These can be the depth and diffusion of financial loss and the duration of the downturn.
- A bear market usually comes to an end when prices reach a point where they can no longer drop and investor sentiment begins to rise. Consumer and business confidence rise as well and market prices begin a long climb.
- When stocks gain twenty percent from the recent low, a bull market sets in marking a broad recovery in the market.
- Bear markets can be difficult to trade in especially for inexperienced traders. It’s hard to predict when the bear market will end and when the bottom price has been reached, since rebounding is a slow and unpredictable process that may be influenced by a number of external factors.
Opportunities in bear markets
- Bear markets, however, present opportunities. If your investment strategy is long-term. Buying during this market can pay off when the cycle is reversed.
- Advanced investors can use strategies like short selling which is a way of betting that an asset will decline in price.
- While there have been several bear markets in the U.S, the economy generally spends more time expanding than contracting. This means that the market spends more time as a bull than a bear.
Examples Great depression bear market
1929 stock market crash.
- This was the worst in U.S. history and was caused by the 1929 stock market crash.
- This was followed by the popping of an asset known as buying on margin which allowed people to borrow money from their broker and only put down ten to twenty percent of the stock value.
2008 bear market
- This was the second-worst by percentage and was caused by the 2008 stock market crash.
- the failure of several financial and insurance institutions and the reluctance of Congress to restore confidence by passing a bailout.
- It came to an end in 2009 when the government launched the economic stimulus plan.
2020 bear market
Trend reversible
- Bear markets come after bull markets. After some time, bull markets reach a point where investors experience irrational exuberance, causing prices to escalate.
- Assets being traded on the market are overvalued and investors start to anticipate falling prices. They begin to sell their investments, causing prices to fall.
- This loss of confidence can be caused by falling housing prices, economic circumstances, high-interest rates, natural events or anything that shatters positive sentiment.
A bear market causes many investors to switch to an investing strategy of maintaining their capital instead of growing it.
During a bear market, instead of investing in stocks, some might try to capitalise on assets that have had better returns.

Precaution during bear markets
- One can get ready for a bear market by reducing risk in their portfolio. You could do this by increasing the amount of cash and reducing the number of growth stocks in your portfolio.
- You can also choose mutual bonds or bonds that perform better during a bear market.
- Individual bonds are safer than bond funds during a bond bear market. The reason for this is that their interest rates and payments are fixed. If you hold onto them until they mature you’ll receive the promised amount unless the person issuing defaults.
While the stock market has experienced sustained periods of growth and decline, along with blips and market corrections, it has historically performed well.
But past performance is no guarantee of future results. Understanding the direction the market in Bear and Bull Markets is taking and having a carefully constructed long-term plan and diversified portfolio can help you manage the ebbs and flows of the market and achieve sustained success.
Why is it called bull bear market?
The terms bull bear market are often used to describe general actions and attitudes either of an individual asset or the market as a whole.Bull will thrust its horns up into the air, while a bear will swoop down. These actions have been metaphorically attributed to the movement of a market.
Which is a bear market?
The opposite of a bull market is a bear market. It is characterised by falling prices and is typically shrouded in pessimism.
What are bull bear and pig in stock market?
Bull refers to a rising market, bear refers to a falling market, and pig refers to a greedy investor who ignores long-term strategies.
What does 20% bull market mean
A 20% bull market means that the stock market has experienced a sustained increase in prices, resulting in a rise of 20% or more from previous lows.